Preventing Leaks & Contamination: A Risk-Based Approach to Single-Use System Integrity
Preventing Leaks & Contamination: A Risk-Based Approach to Single-Use System Integrity

Single-use systems (SUS) are vital in modern bioprocessing. They offer adaptability, reduce cleaning needs, and speed up operations. However, keeping these systems intact is crucial. It ensures product purity and process dependability. Leak-free performance is necessary from production to use. This prevents expensive contamination issues.
The Importance of Single-Use System Integrity in Bioprocessing
As biopharmaceutical production embraces disposable tools, ensuring system strength is a top concern for quality and safety. A strong system avoids leaks that could harm the product or process.
Key Drivers Behind the Adoption of Single-Use Technologies
Several reasons fuel the rise of single-use tools. They lower the chance of product mixing, cut equipment costs, save water and energy, and allow flexible operations. These benefits suit facilities making multiple products or small-scale batches. Quick changeovers make them ideal for such settings.
Risks Associated with Leaks and Contamination
Leaks in single-use systems can allow germs to enter or cause product loss. Even tiny cracks can ruin purity, leading to failed batches or rule-breaking. These issues can halt production and raise costs.
Regulatory Expectations for System Integrity
Agencies like the FDA and EMA require proof that single-use systems work well during use. Following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), United States Pharmacopeia (USP), and European Pharmacopeia (EP) rules is key. Validated tests for container closure strength are mandatory to meet these standards.
Risk-Based Strategies for Ensuring Integrity
A forward-thinking plan based on risk evaluation pinpoints where testing matters most. This approach strengthens system reliability.
Identifying Critical Control Points in the Process
Critical control points (CCPs) are stages where a break could cause contamination or purity loss. These include links between bags and filters, tubing welds, or connections between single-use parts and metal equipment. Identifying these spots focuses testing efforts.
Categorizing Risk Levels Based on Product Sensitivity and Process Stage
Products vary in how easily they get contaminated. For example, live cell cultures need stricter purity than simple solutions. Early production stages may allow slight risks, but final filling demands tight control. Sorting risks helps choose the right testing methods.
Implementing Preventive Measures Based on Risk Assessment
Preventive steps reduce risks. These include checking suppliers, ensuring material suitability, training workers, or testing systems before use. For instance, a pre-use pressure test on a bag confirms it holds up before filling with valuable product. Such actions catch issues early.
Methods for Detecting Leaks in Single-Use Systems
Choosing the right leak detection method depends on system design, needed precision, and regulatory rules. Each method has strengths and limits.
Overview of Common Leak Detection Techniques
Several ways exist to find leaks in single-use systems:
- Pressure Decay Testing: This involves filling a closed system with air and watching for pressure drops. It’s simple but may miss tiny leaks.
- Vacuum Decay Testing: This uses a vacuum instead of air pressure. It detects smaller leaks better than pressure testing.
- Espectrometría de masas con helio: This highly precise method uses helium to find tiny leaks. It needs special tools and controlled settings.
- Visual Inspection and Dye Penetration: These methods use dye or light to spot leaks. They’re affordable but less reliable due to human error.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Helium testing is very accurate but costly for regular use. Pressure and vacuum tests balance precision and practicality. They need proper setup to work well. Visual checks are helpful but not dependable alone due to their subjective nature.
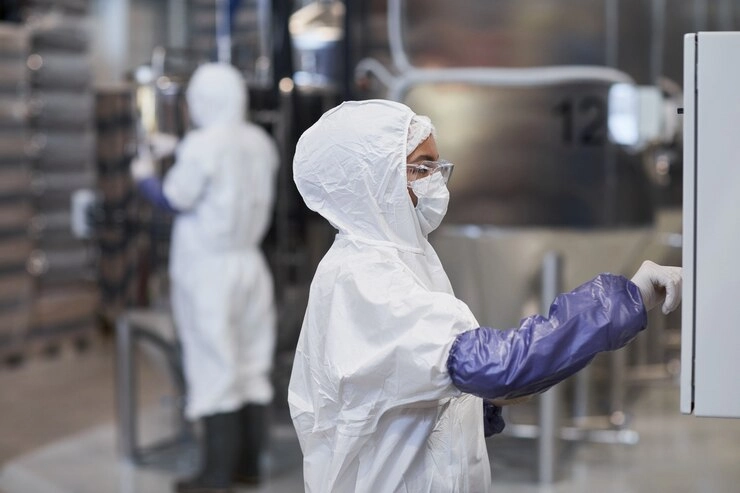
Role of Packaging Leak Testers in Quality Assurance
Packaging leak testers are key to checking system strength before production. They ensure containers stay sealed under real-world conditions.
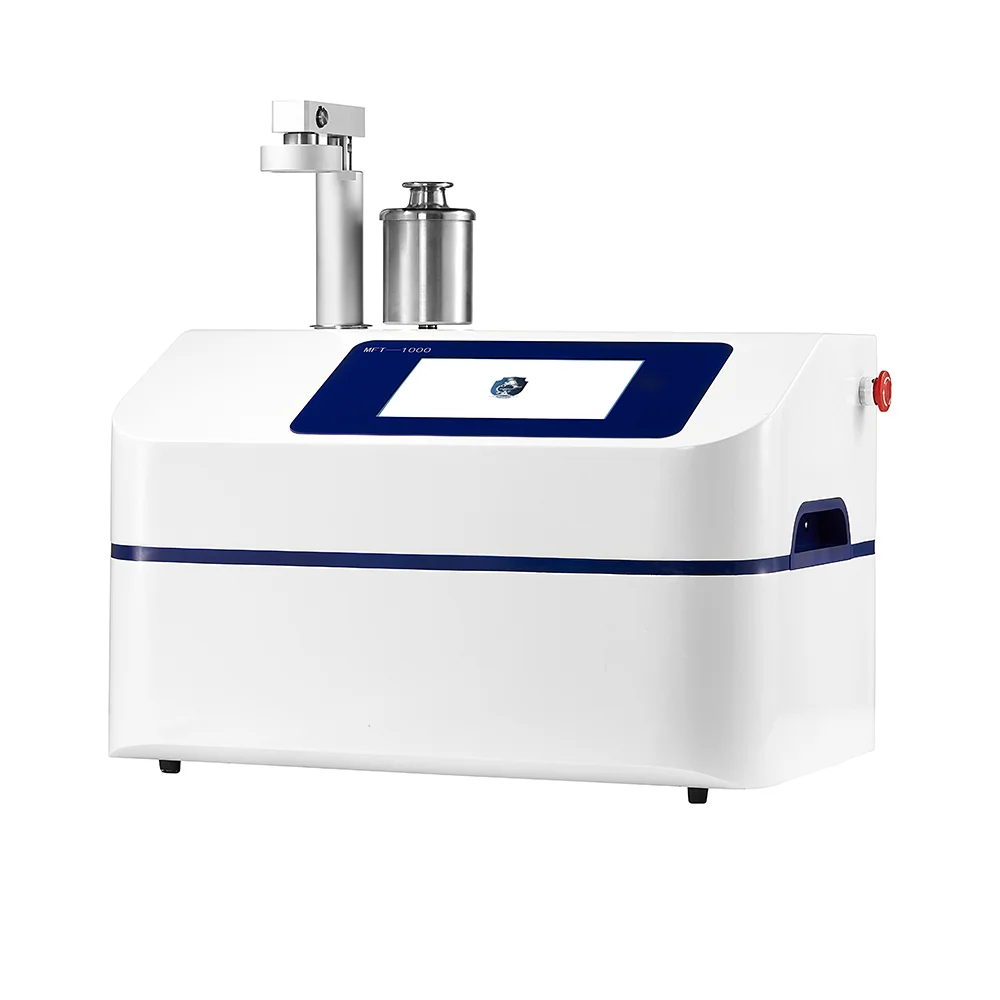

How Packaging Leak Testers Support Sterility Assurance
These testers verify that containers like bags hold tight under stress, such as pressure changes or transport strain. This confirms the system prevents contamination, protecting product purity.
Integration into Quality Control Workflows
Leak testers fit into quality checks at multiple stages. These include inspecting supplies, verifying assemblies before sterilization, or final checks before cleanroom use. Early detection avoids delays in production.
Enhancing Process Reliability with Automated Testing Solutions
Automated testers reduce errors from manual checks. They allow fast, consistent testing across many units. This ensures steady results without human mistakes, boosting process dependability.
Best Practices for Maintaining System Integrity Throughout the Lifecycle
Keeping single-use systems intact requires care from purchase to disposal. Consistent practices ensure reliability.
Supplier Qualification and Material Traceability
Choose trusted suppliers with strong quality controls. Records should track material details, sterilization history, and shelf life. This helps find causes if problems occur later.
Storage, Handling, and Installation Guidelines
Improper storage, like exposure to sunlight or extreme heat, can weaken materials. During setup, check seals and connections for damage. Proper handling in cleanrooms prevents accidental harm or contamination.
Routine Monitoring and Documentation Practices
A solid plan includes testing systems before use. For example, check filters for every batch and inspect during operation. Keep detailed records to track performance and meet regulatory needs.
MedIntegrity: Reliable Partner in Leak Detection Solutions
Integridad médica provides specialized tools for packaging in bioprocessing. Their solutions ensure system strength and compliance.
Company Overview and Industry Focus
MedIntegrity creates high-quality testing tools for pharmaceutical packaging, including single-use systems for sterile production. Their focus is on reliable, industry-specific solutions.
Features of MedIntegrity’s Packaging Leak Tester Solutions
MedIntegrity’s tools stand out for their quality:
- Compliance with FDA, GMP, USP, and EP Standards: Their testers meet strict rules, including FDA 21 CFR Part 11. They provide records ready for audits worldwide.
- Customization Options for Specific Applications: Their testers work for flexible bags or rigid containers. They adjust to specific shapes or production needs.
- Support Services: Installation, Training, Maintenance: MedIntegrity offers on-site setup, worker training, and ongoing maintenance. This ensures tools work reliably in regulated settings.
Preguntas frecuentes
Q1: What is a packaging leak tester used for?
A: It checks if containers like single-use bags stay sealed under conditions like pressure or vacuum. This prevents contaminants from entering sterile areas.
Q2: How often should single-use system components be tested for leaks?
A: Testing depends on risk evaluation, not a set schedule. Since components are single-use, they’re not tested repeatedly. Instead:
- Supplier Level: Manufacturers validate component strength.
- Pre-use Testing: High-risk parts, like sterile filters or final bags, are tested before each use (every batch).
- Lower-risk parts: May skip pre-use tests if supplier data is reliable, based on risk assessment.
Q3: Can automated leak testers replace manual inspection entirely?
A: Automated testers reduce errors by standardizing tests. However, they work best with visual checks. Visual inspections catch external damage that pressure tests might miss.